Blog Posts
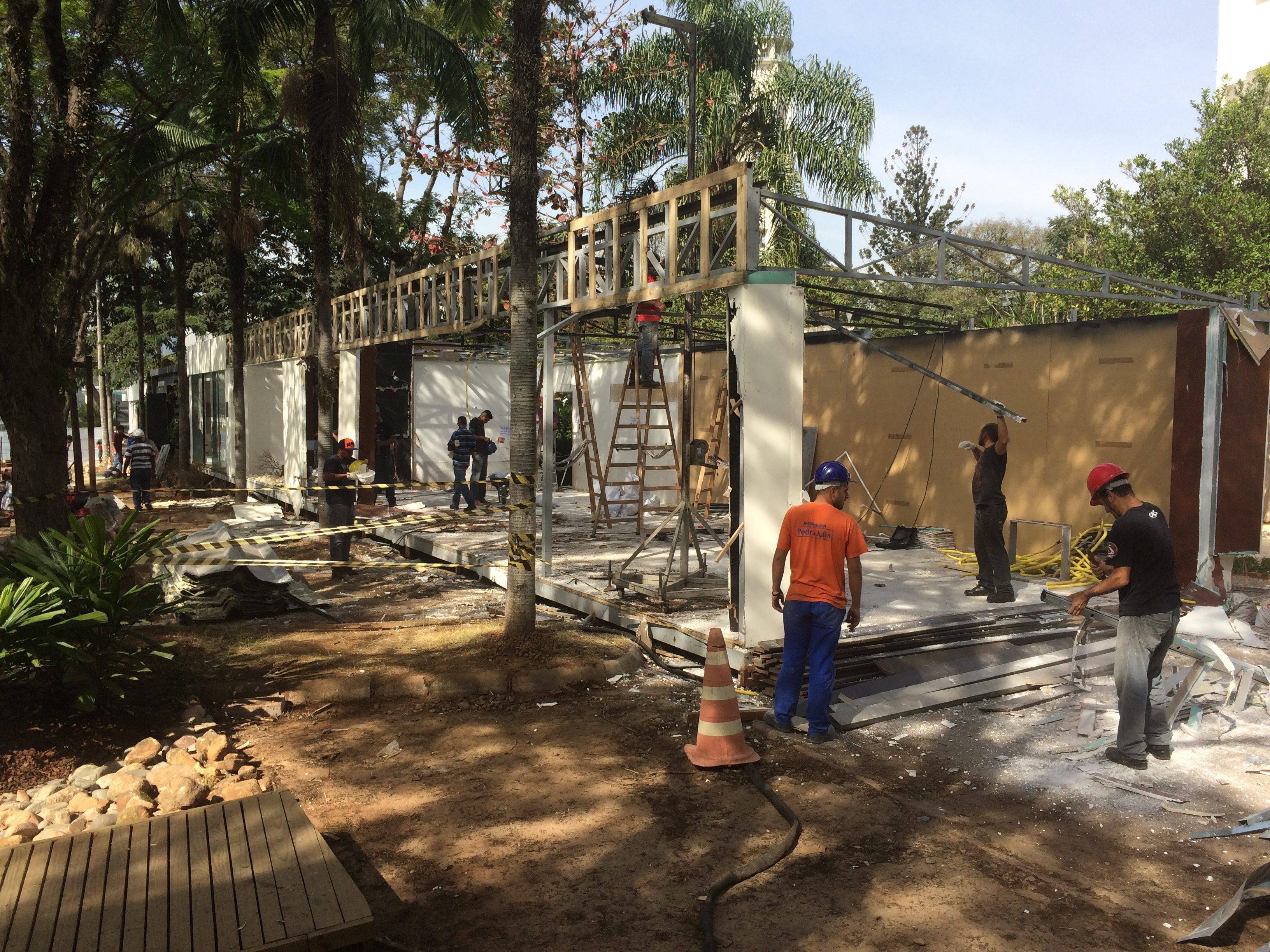
CASACOR 2016
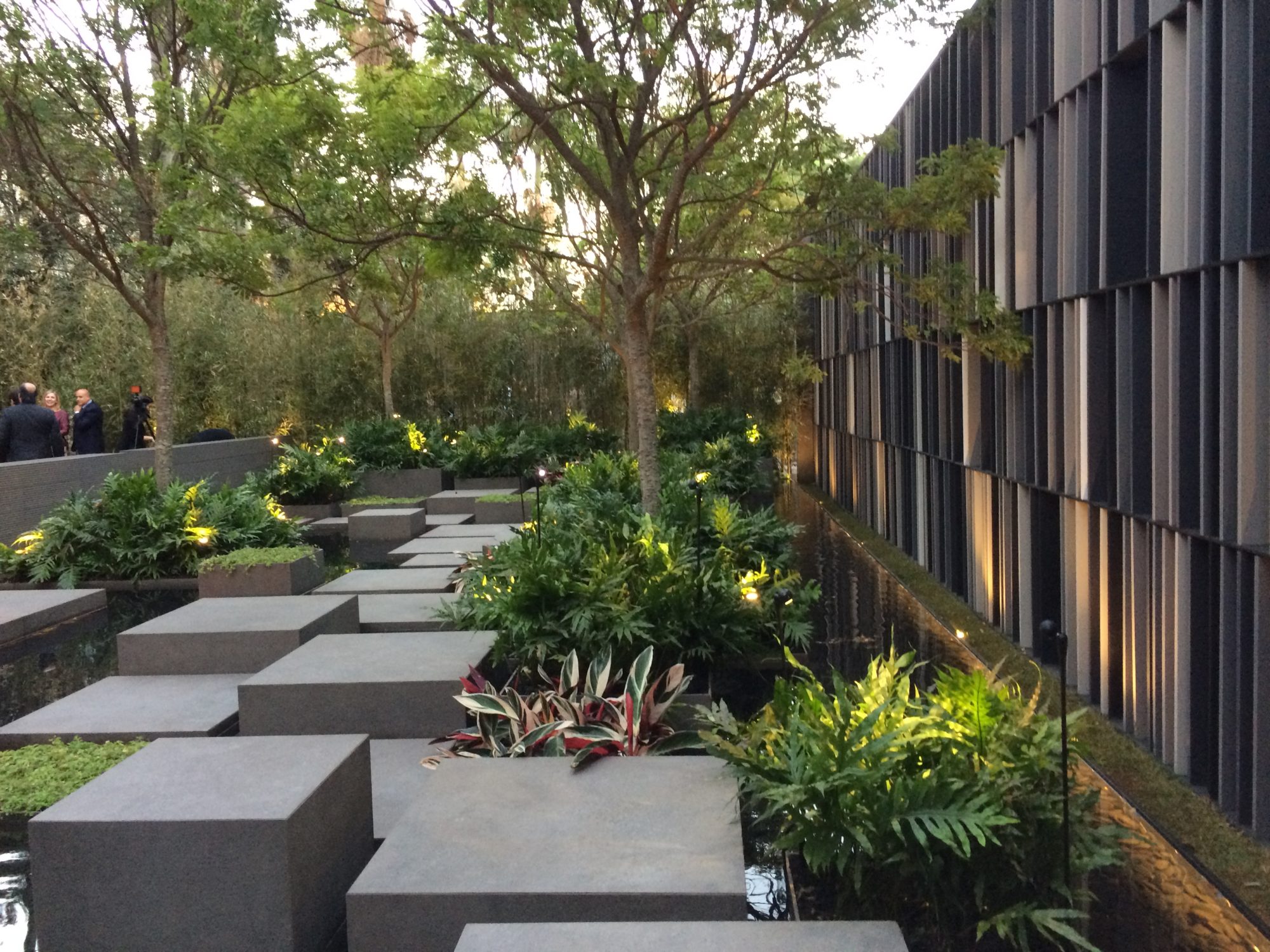

CASACOR 2016
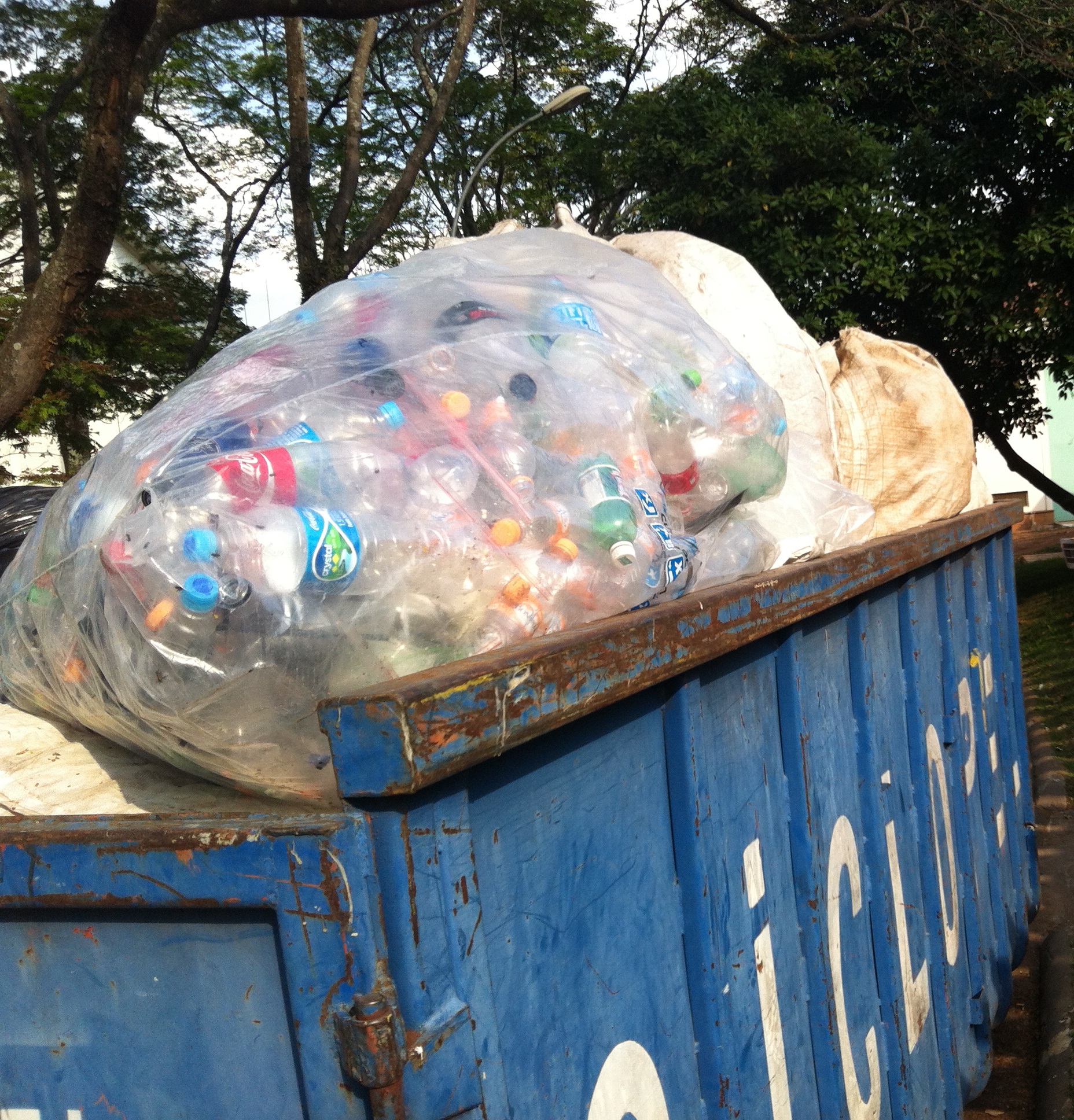
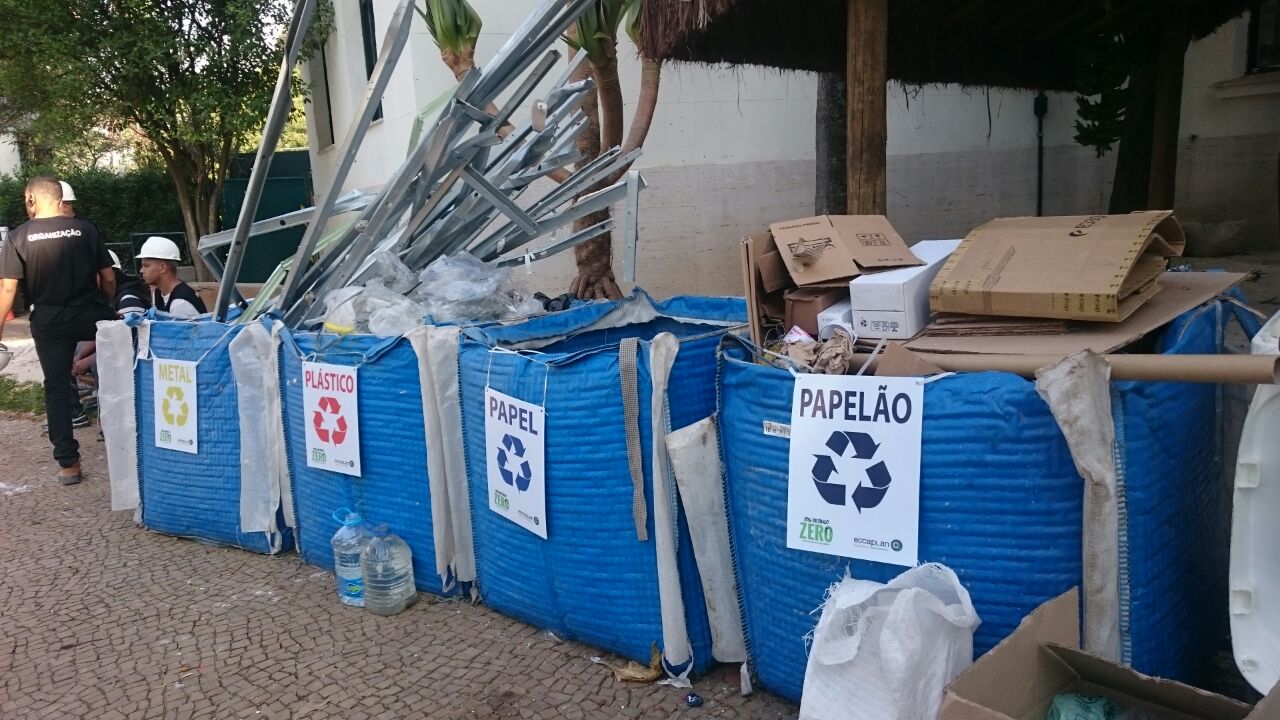
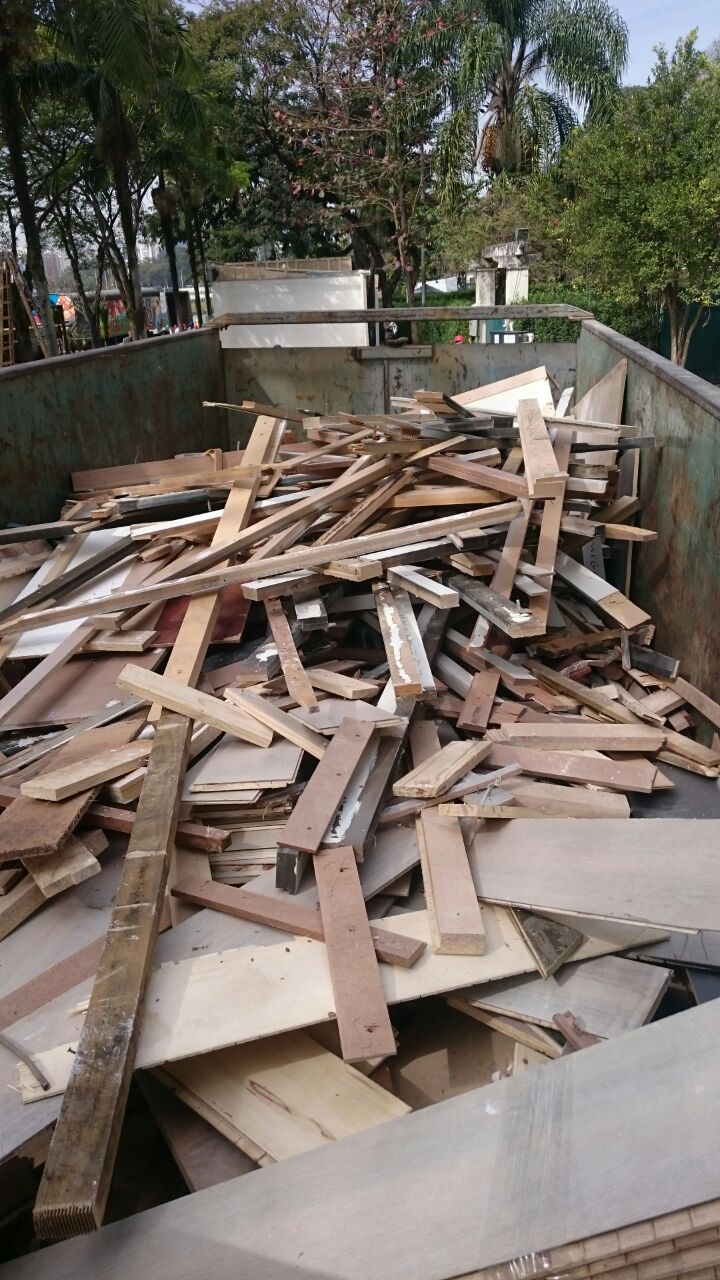
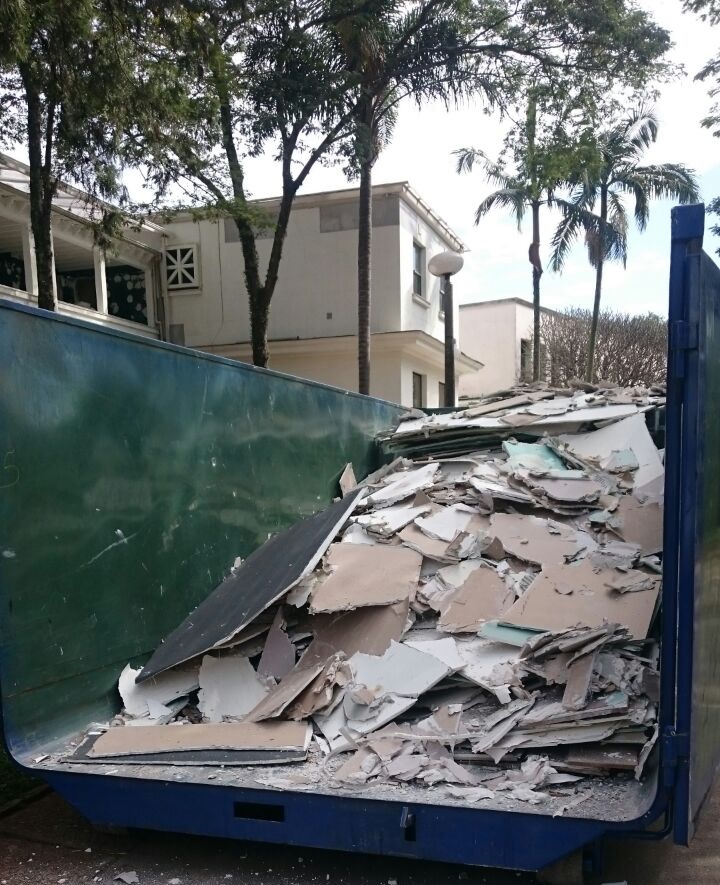
Separation and recycling of construction and demolition waste, recyclable waste and organic composting. More than 90% of the waste was diverted from landfills.
Composting of organic material during the exhibition and recycling of all waste produced during assembly, exhibition and dismantling:
Construction and demolition waste separated by a bucket and intended for recycling: rubble, wood, plaster and scrap metal.
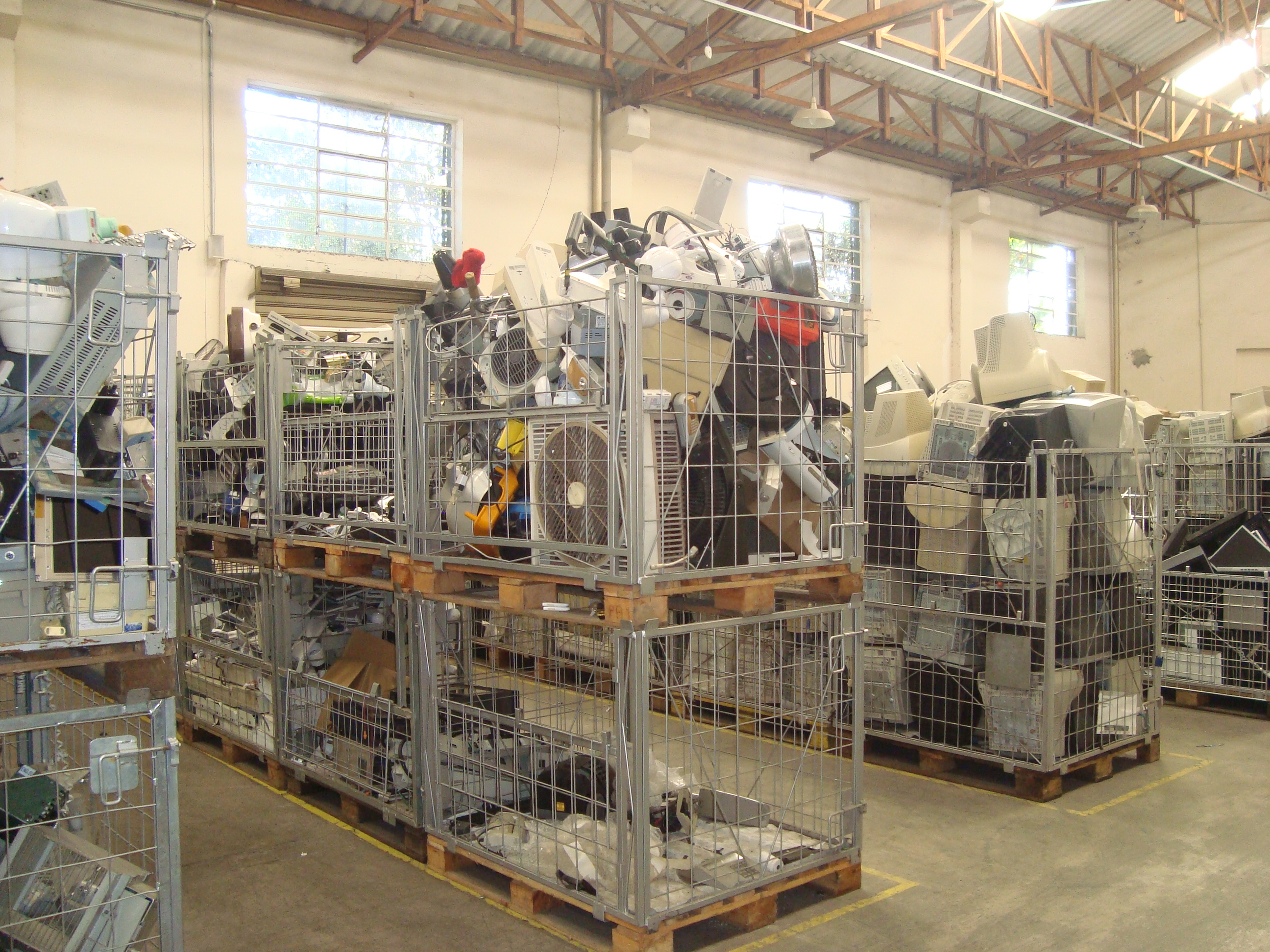
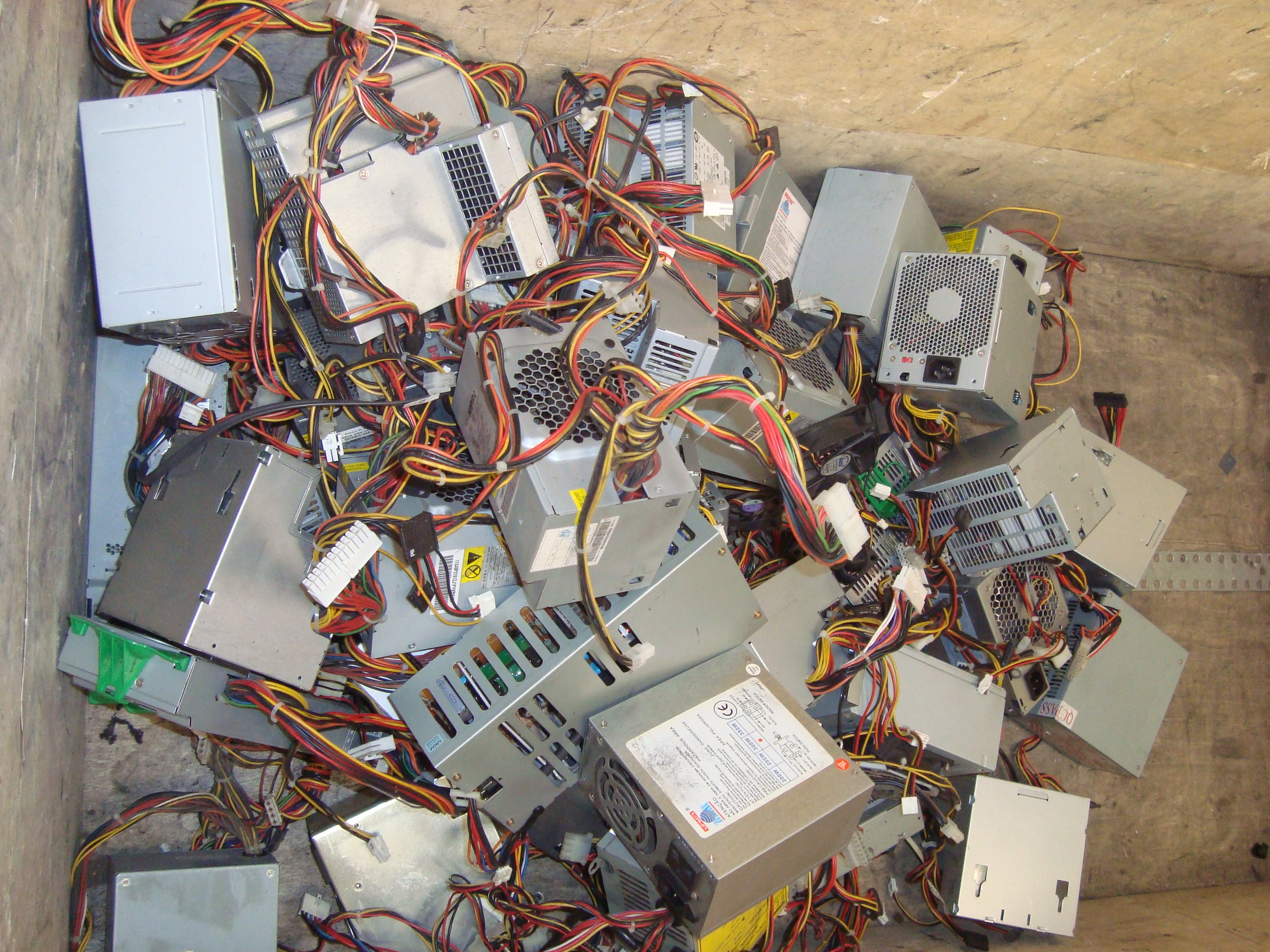
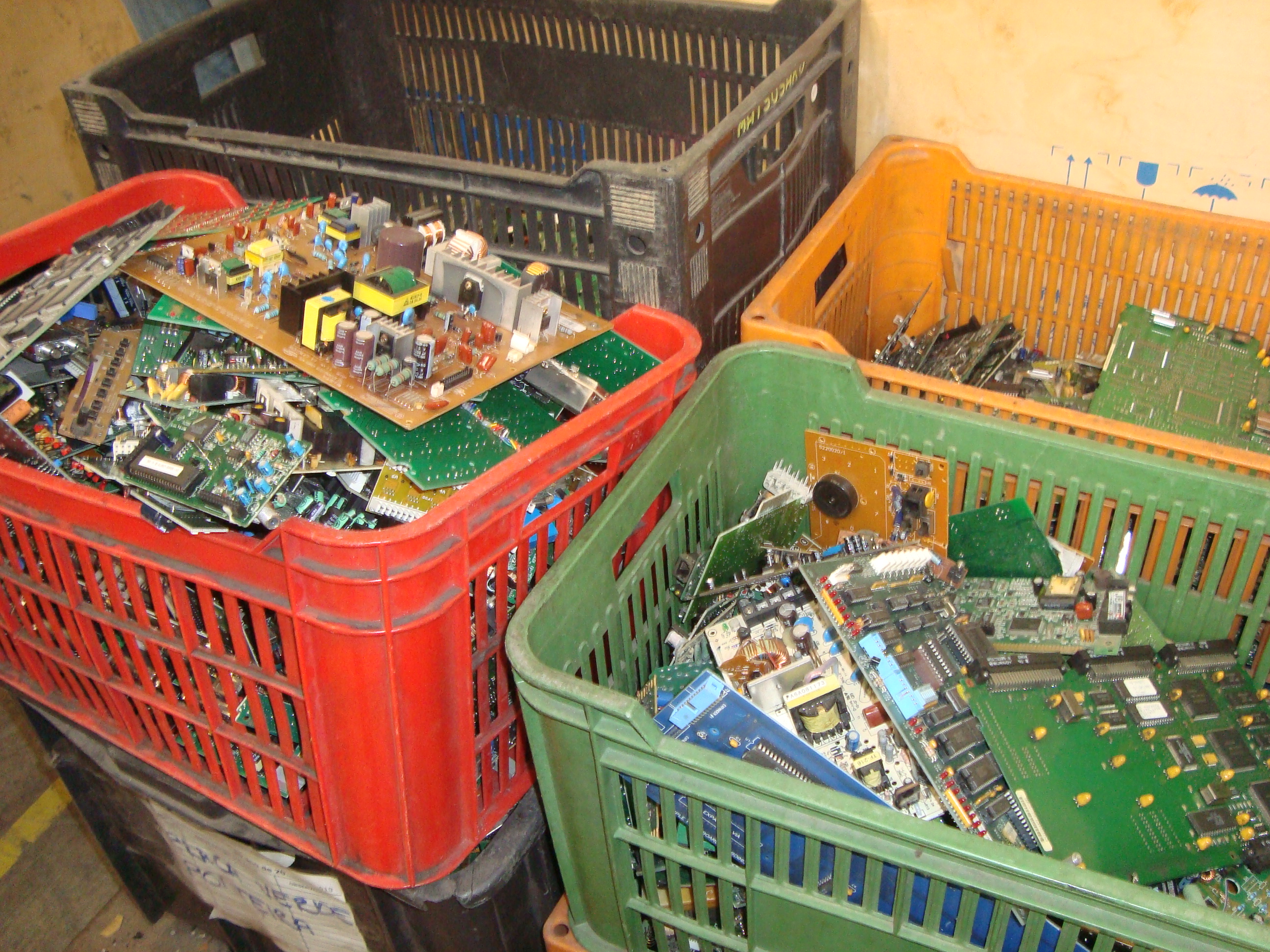
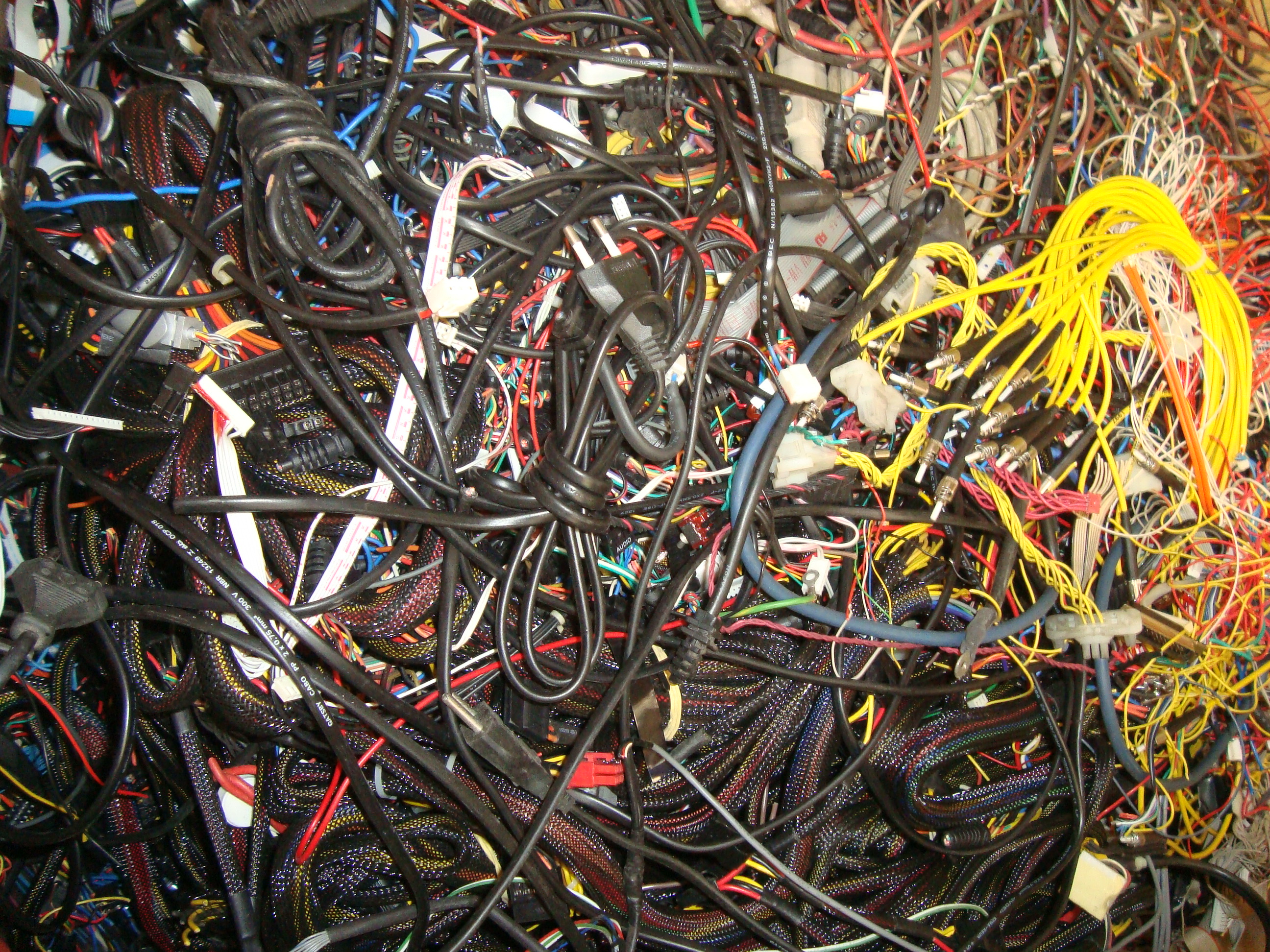
Eletronic waste
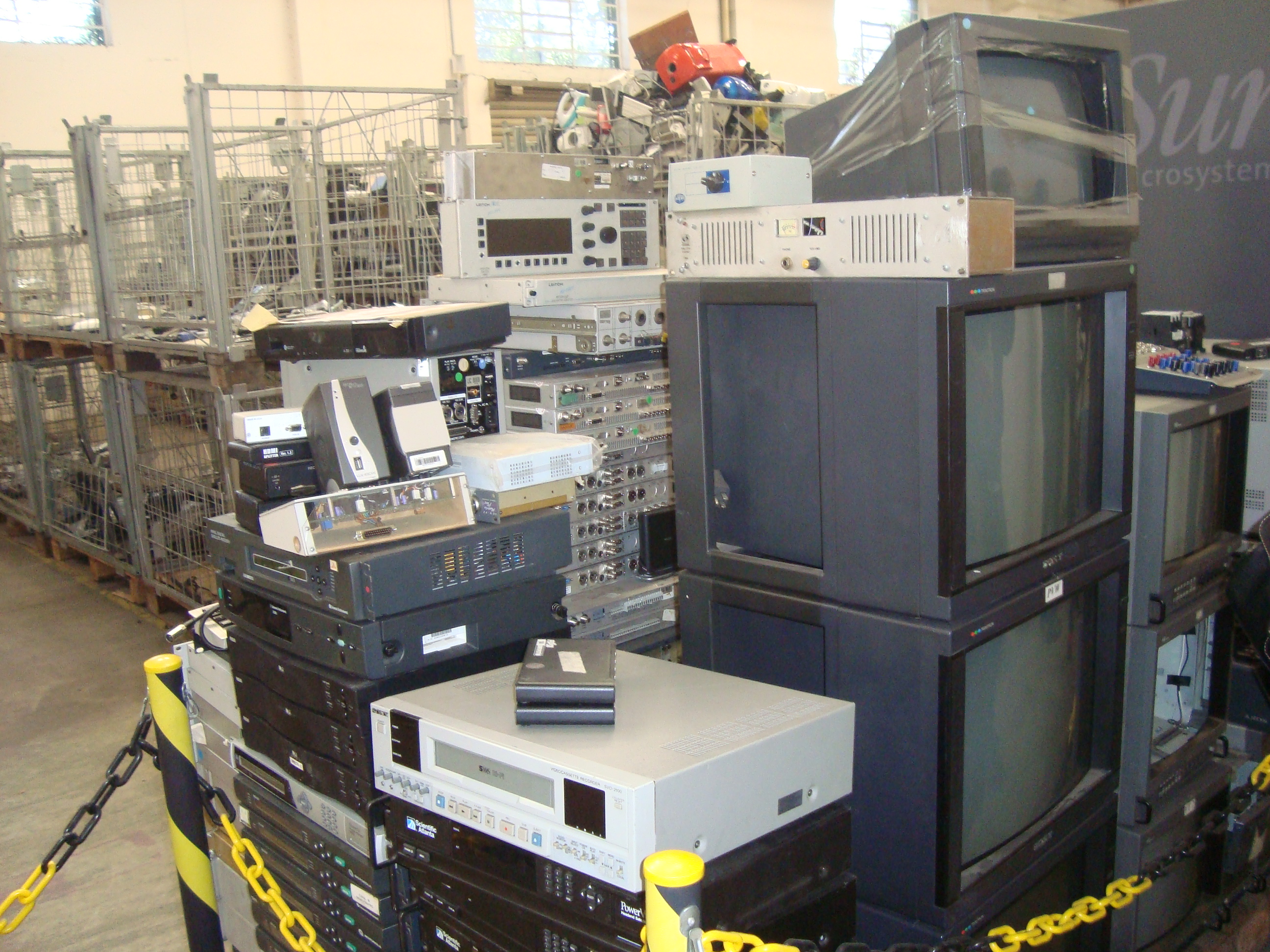

How to properly dispose of electro-electronic waste?
If you have electro-electronic equipment that is broken or unused and you do not know how to dispose of it, look for a cooperative or a voluntary delivery point that receives this material.
I would like to recommend the work of Coopermiti, a registered São Paulo cooperative. They collect electroelectronic waste in large quantities from collection points and large generators and also receive the material on site.
E-waste delivery locations:
Coopermiti
(11) 3666-0849 / 99301-7696 – Rua João Rudge, 366 – Casa Verde
Pontos de coleta da Coopermiti:
CEU FORMOSA – (11) 2216-4622 – Rua Sargento Claudiner Evaristo Dias, 10 – Parque Santo Antônio
COLÉGIO HEITOR GARCIA – (11) 3853-4996 – Rua Roma, 350 – Lapa – CEP 05005-090 – Horário de funcionamento para o descarte: 7 às 19 h.
CONTINENTAL SHOPPING – 4040-4981 / 2666-3830 – (pequenos objetos) Av. Leão Machado, 100 – Jaguaré
ETEC PINHEIROS – APM – Escola Técnica Estadual Guaracy Silveira – (11) 3813-3986 Rua Ferreira de Araújo, 527 – Pinheiros
E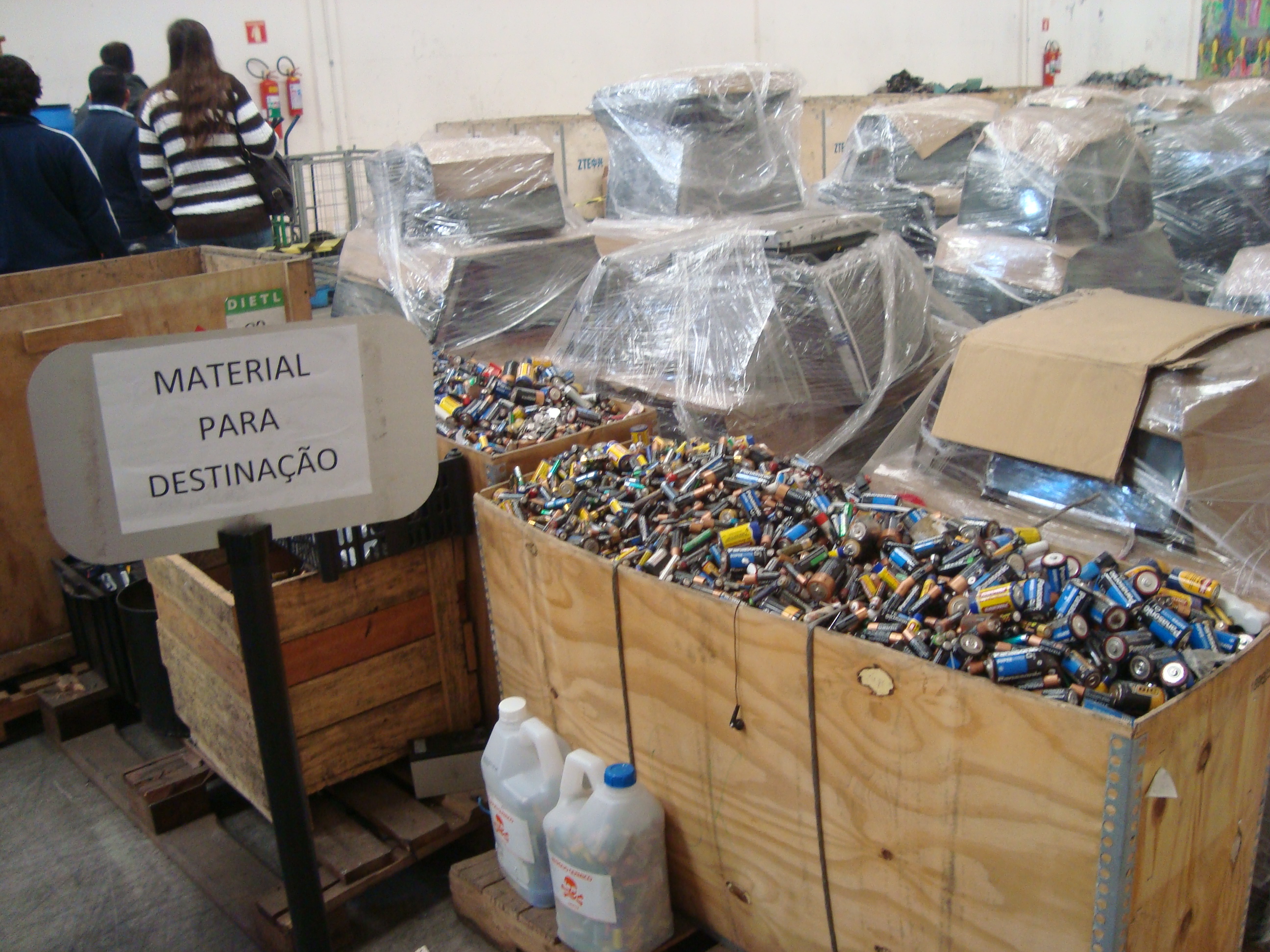 TEC Vila Formosa – (11) 2211-6485 – Rua Bactória, 38 – Jardim Vila Formosa
TEC Vila Formosa – (11) 2211-6485 – Rua Bactória, 38 – Jardim Vila Formosa
PAÇO CULTURAL JULIO GUERRA – (11) 5523-6455 – Praça Floriano Peixoto, 131 – Santo Amaro
PARQUE LUIS CARLOS PRESTES – (11) 3721-4965 – Rua João Della Manna, 665 – Butantã
PARQUE DA PREVIDÊNCIA – (11) 3721-8951 – Rua Pedro Peccinini, 88 – Jardim Previdência
PARQUE ALFREDO VOLPI – (11) 3031-7052 – Rua Engenheiro Oscar Americano, 480 – Morumbi
SANTANA PARQUE SHOPPING – (11) 2238-3002 (pequenos objetos) – Rua Conselheiro Moreira de Barros, 2.780 – Santana
* Materials not received: lamps, TVs and monitors open or cracked, leaking chemical component.
* Do not collect only batteries, but if they are with e-trash at the time of collection, they are part of the Abinee program.
* Offering service for the following items on a budget:
– Monitor and TV CRT, Monitor and TV LCD, Fiber optic, Magnetic tapes (DAT, VHS, K7, BETACAM, DISQUETES, etc …), toner and ink cartridge.
Homemade Composter

Homemade composter – Do it yourself!
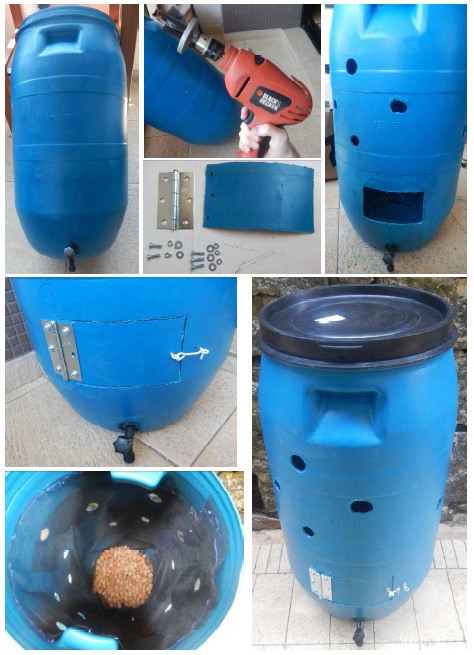
 I’m sharing the step-by-step photos of a 100 liter composter that can be used in homes.
I’m sharing the step-by-step photos of a 100 liter composter that can be used in homes.
You will need: 100 liter plastic bottle with faucet; mosquito net (1m); hinge, 6 bolts, 6 washers and 6 nuts for the fertilizer catching door; scissor, stiletto, drill, saw-glass; expanded clay.
What you can put in the compost:
Green (rich in nitrogen)
• Green leaves, grass, flowers
• Garden pruning, plants in general
• Remains of food
• Residues of fruit and vegetable
• Remains of bread crumbs, cookies, cereals
• Remains of cooked grains, flour, pasta and rice
• Coffee eraser (including dishwasher), tea bags …
• Manure of cattle, pigs, goats, sheep and chickens
• Eggshells
MARRONS (rich in carbon)
• Sawing of wood, branches and bark of trees
• Cardboard, Newsprint
• Remains of dry pruning, dry leaves, grass and dry grass
• Cardboard boxes, cardboard, napkins
• Wood shavings
• Corn and banana straw, hay, straw
Do not place in the composter:
• Human and pet urine and faeces
• Chemicals in general
• Remains of meat or fish, bone and pimples (can attract rodents and cockroaches)
• Used toilet paper or diapers
• Ashes and cigarette butts
• Fats and dairy products (can attract rodents and cockroaches)
• Varnished wood, glass, metal
• Cooking oil, other oils, paints, plastics, plastic paper
• Remains of very temperate food
• Invasive herbs and veggies with pests
• Medicines
How to compost::
1. The place to install the composter: If it is possible, place the composter near the kitchen; so the disposal of leftover food becomes easier. It is important that it stays in an airy and shaded place, for example under a tree.
2. Materials to compost: Collect and mix suitable green and brown materials for composting. We should have twice as many brown elements as green ones. Add a little bit of sawdust, dry straw, dry leaf or cardboard to the compost each day as a cover, leaving the green materials underneath.
3. Controlling the composting process: In order to develop well, the microorganisms need adequate conditions of scouring, humidity and temperature. The organic remains should be moist but not wet. If the material becomes very dry we will put some water. We should stir the material once or twice a week to allow sandblasting. We must control so that the temperature does not exceed 70 degrees. If it does, scrape the materials.
4. How to know if the compost is ready? At the end the compost should have an aspect which can not distinguish the types of material. It should have the dark color and smell of earth. When we rub on our hands, they do not get dirty. The process takes on average 2 months.
5. The slurry, or biofertilizer, can be used to combat pests in the garden. Just dilute the biofertilizer. There are 20 parts of water for a part of biofertilizer.














 Português
Português
Recent Comments